Searching in Linked List
Sequential search is the most common search used on linked list structures.Algorithm
Step-1: Initialise the Current pointer with the beginning of the List. Step-2: Compare the KEY value with the Current node value; if they match then quit there else go to step-3. Step-3: Move the Current pointer to point to the next node in the list and go to step-2, till the list is not over or else quit.
Example
/*Search An Element in Linked List*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
}
first, *nw;
int search(int);
void main()
{
int no,i,item,pos;
clrscr();
first.next=NULL;
nw=&first;
printf("Enter The No of nodes, you want in linked list: ");
scanf("%d",&no);
printf("\n");
for(i=0;i< no;i++)
{
nw->next=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
printf("Enter element in node %d: ",i+1);
scanf("%d",&nw->data);
nw=nw->next;
}
nw->next=NULL;
printf("Linked list is:\n");
nw=&first;
while(nw->next!=NULL)
{
printf("%d\t",nw->data);
nw=nw->next;
}
printf("\n");
printf("Enter item to be searched : ");
scanf("%d",&item);
pos=search(item);
if(pos<=no)
printf("Your item is at node=%d",pos);
else
printf("Sorry! your item is not in linked list.");
getch();
}
int search(int item)
{
int count=1;
nw=&first;
while(nw->next!=NULL)
{
if(nw->data==item)
break;
else
count++;
nw=nw->next;
}
return count;
}
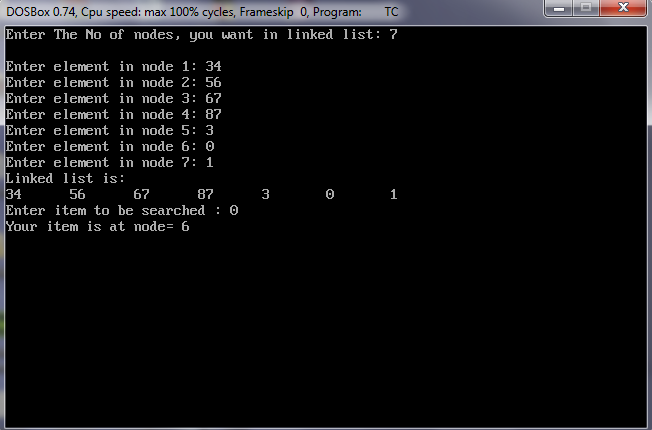
Output