Quick sort
Quicksort is a simple sorting algorithm using the divide-and-conquer recursive procedure.It is the quickest comparison-based sorting algorithm in practice with an average running time of O(n log(n)).It is also known as partition-exchange sort.
Algorithm
QUICKSORT(A, p, r) 1. if p < r 2. q = PARTITION(A, p, r) 3. QUICKSORT(A, p, q - 1) 4. QUICKSORT(A, q + 1, r) PARTITION(A, p, r) 1. x = A[r] 2. i = p - 1 3. for j = p to r - 1 4. if A[j] <= x 5. i = i + 1 6. exchange A[i] with A[j] 7. exchange A[i + 1] with A[r] 8. return i + 1
Quick sort Implementation
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void quicksort(int arr[], int lb, int ub);
void main()
{
int arr[20], n, i;
clrscr();
printf("\n\t\t\t------Quick Sort------\n\n");
printf("Enter the size of the array:");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("Enter the elements to be sorted:\n");
for(i=0;i < n;i++)
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
quicksort(arr, 0, n-1);
printf("\n\t\t\t-----Quick Sorted Elements-----\n\n");
printf("Sorted array:");
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("\t%d ",arr[i]);
getch();
}
void quicksort(int arr[], int lb, int ub)
{
int pivot, i, j, temp;
if(lb < ub)
{
pivot = lb;
i = lb;
j = ub;
while(i < j)
{
while(arr[i] <= arr[pivot] && i <= ub)
i++;
while(arr[j] > arr[pivot] && j >= lb)
j--;
if(i < j)
{
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[pivot];
arr[pivot] = temp;
quicksort(arr, lb, j-1);
quicksort(arr, j+1, ub);
}
}
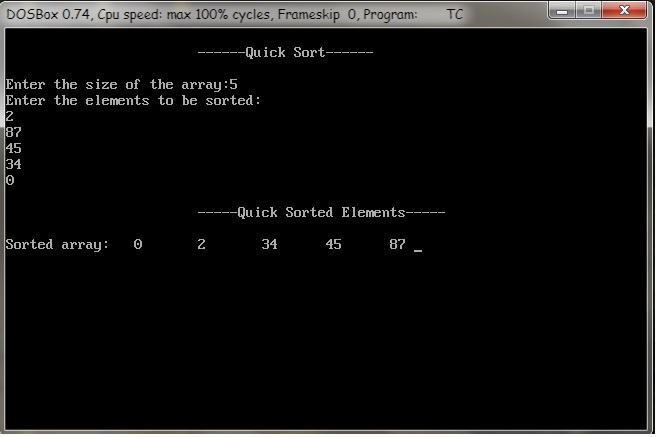
OUTPUT