Implementation
1.In c language, memory can be acquired through the malloc() and calloc() function.
2.Memory acquired during run-time can be freed through the free() function.
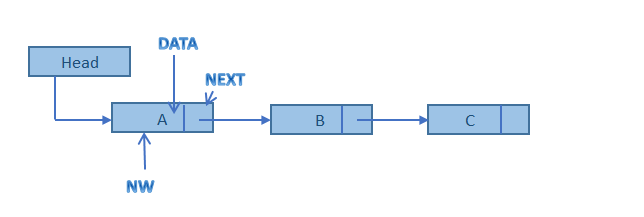
node *nw; nw=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); nw->data=A,B,C; nw->next=100,200,Null;
Implementation Of Linked list
/*implements of single link list*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<alloc.h>
struct node
{
int no;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *first;
void creatlist()
{
char ch='y';
struct node *ptr,*nw;
while(ch!='n')
{
printf("\nEnter item in list");
nw=(struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
scanf("%d",&nw->no);
nw->next=0;
if(first==0)
{
first=nw;
}
else
{
for(ptr=first ;ptr->next!=0;ptr=ptr->next);
{
ptr->next=nw;
}
}
printf("\nDo you want to countinue y\n");
ch=getch();
}
}
void display()
{
struct node *ptr;
printf("Item int list are");
for(ptr=first;ptr!=0;ptr=ptr->next)
{
printf("\n%d",ptr->no);
}
}
void main()
{
clrscr();
first=0;
creatlist();
display();
getch();
}
Output
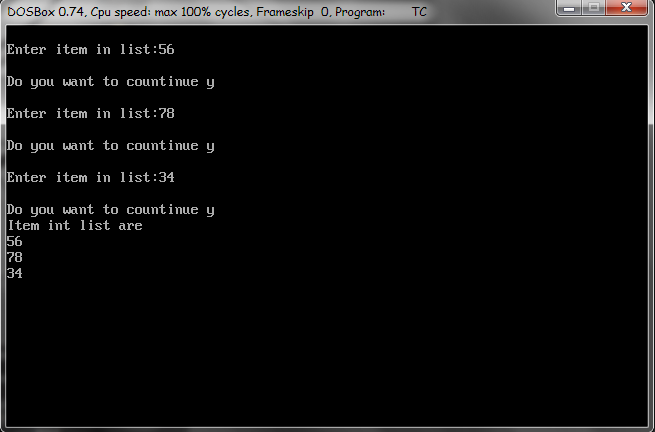
Creating a linked list
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<alloc.h>
struct node
{
int data;
struct node * next;
};
void main()
{
struct node * nw, * head;
int i, n;
clrscr();
head = 0 ;
printf("Enter the size of list");
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=0;i < n;i++)
{
printf("Enter the Element");
nw = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
scanf("%d",&(nw->data));
nw->next = head;
head = nw;
}
nw = head;
while(nw)
{
printf("%d\n", nw->data);
nw = nw->next ;
}
getch();
}
Counting nodes in a list
int count(node nw)
{
int i;
i=0;
while(nw!=NULL)
{
i=i+1;
nw=nw->next;
}
}
