Prim's Algorithm
Prim's algorithm is a greedy algorithm that finds a minimum spanning tree for a connected weighted undirected graph.It finds a subset of the edges that forms a tree that includes every vertex, where the total weight of all the edges in the tree is minimized.
This algorithm is directly based on the MST( minimum spanning tree) property.
Example
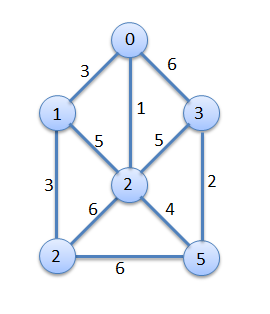 |
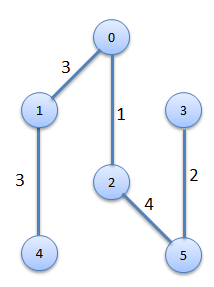 |
| A Simple Weighted Graph | Minimum-Cost Spanning Tree |
Prim's Algorithm
MST-PRIM(G, w, r) 1. for each u V [G] 2. do key[u] ← ∞ 3. π[u] ← NIL 4. key[r] ← 0 5. Q ← V [G] 6. while Q ≠ Ø 7. do u ← EXTRACT-MIN(Q) 8. for each v Adj[u] 9. do if v Q and w(u, v) < key[v] 10. then π[v] ← u 11. key[v] ← w(u, v)
Example

Procedure for finding Minimum Spanning Tree
Step1
|
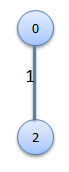 |
Step2
|
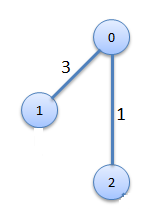 |
Step3
|
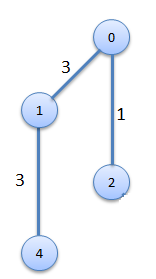 |
Step4
|
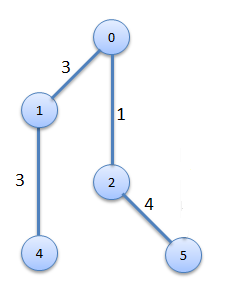 |
Step5
|
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Cost = 1+2+3+3+4 = 13 |
C IMPLEMETATION of prim's Algorithm
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int a,b,u,v,n,i,j,ne=1;
int visited[10]={0},min,mincost=0,cost[10][10];
void main()
{
clrscr();
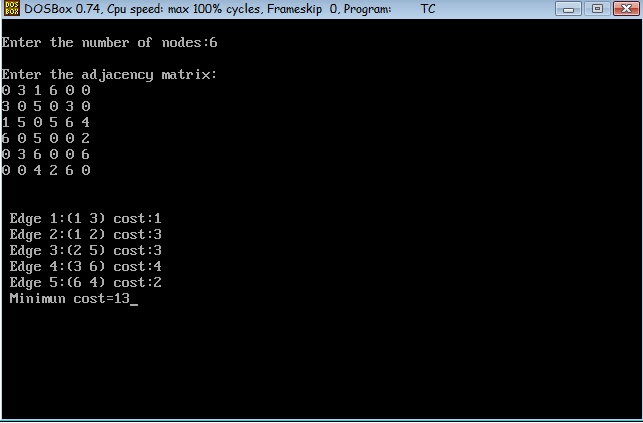
printf("\nEnter the number of nodes:");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("\nEnter the adjacency matrix:\n");
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&cost[i][j]);
if(cost[i][j]==0)
cost[i][j]=999;
}
visited[1]=1;
printf("\n");
while(ne < n)
{
for(i=1,min=999;i<=n;i++)
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
if(cost[i][j]< min)
if(visited[i]!=0)
{
min=cost[i][j];
a=u=i;
b=v=j;
}
if(visited[u]==0 || visited[v]==0)
{
printf("\n Edge %d:(%d %d) cost:%d",ne++,a,b,min);
mincost+=min;
visited[b]=1;
}
cost[a][b]=cost[b][a]=999;
}
printf("\n Minimun cost=%d",mincost);
getch();
}
output