Dijkstra's Algorithm
Dijkstra's algorithm is a greedy algorithm that solves the shortest path problem for a directed graph G.Dijkstra's algorithm solves the single-source shortest-path problem when all edges have non-negative weights.
Dijkstra's Algorithm
DIJKSTRA(G,s)
1 INITIALIZE-SINGLE-SOURCE(G, S)
2 S ← Ø
3 Q ← V[G]
4 while Q ≠ Ø
5 do u ← EXTRACT-MIN(Q)
6 S ← S U {u}
7 for each vertex v ∈ Adj[u]
8 do if dist[v] > dist[u] + w(u,v)
9 then d[v] ←d[u] + w(u,v)
INITIALIZE-SINGLE-SOURCE( Graph g, Node s )
dist[s] = 0;
for each vertex v in Vertices V[G] - s
dist[v] ← ∞
Example
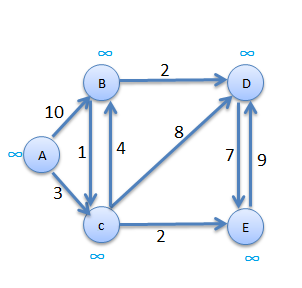
Procedure for Dijkstra's Algorithm
Step1Consider A as source vertex
|
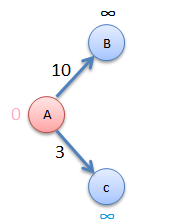
Step2
Now consider vertex C
|
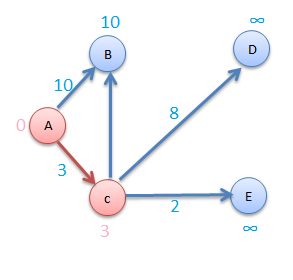
Step3
Now consider vertex E
|
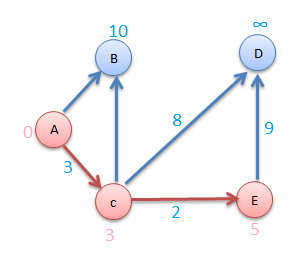
Now consider vertex B
|
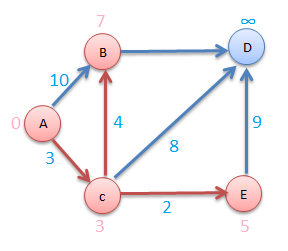
Now consider vertex D
|
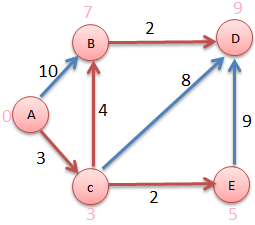
| A | B | C | D | E | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | |
| A | 0 | 10 | 3 | ∞ | ∞ |
| C | 7 | 3 | 11 | 5 | |
| E | 14 | 5 | |||
| B | 9 | ||||
| D | 16 |
C FUNCTION of Dijkstra's Algorithm
void dijikstra(int G[MAX][MAX], int n, int startnode)
{
int cost[MAX][MAX], distance[MAX], pred[MAX];
int visited[MAX], count, mindistance, nextnode, i,j;
for(i=0;i < n;i++)
for(j=0;j < n;j++)
if(G[i][j]==0)
cost[i][j]=INFINITY;
else
cost[i][j]=G[i][j];
for(i=0;i< n;i++)
{
distance[i]=cost[startnode][i];
pred[i]=startnode;
visited[i]=0;
}
distance[startnode]=0;
visited[startnode]=1;
count=1;
while(count < n-1){
mindistance=INFINITY;
for(i=0;i < n;i++)
if(distance[i] < mindistance&&!visited[i])
{
mindistance=distance[i];
nextnode=i;
}
visited[nextnode]=1;
for(i=0;i < n;i++)
if(!visited[i])
if(mindistance+cost[nextnode][i] < distance[i])
{
distance[i]=mindistance+cost[nextnode][i];
pred[i]=nextnode;
}
count++;
}
for(i=0;i < n;i++)
if(i!=startnode)
{
printf("\nDistance of %d = %d", i, distance[i]);
printf("\nPath = %d", i);
j=i;
do
{
j=pred[j];
printf(" <-%d", j);
}
while(j!=startnode);
}
}
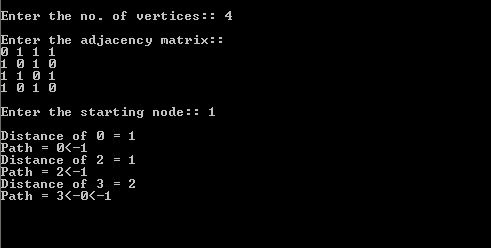
C IMPLEMETATION of Dijkstra's Algorithm
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#define INFINITY 9999
#define MAX 10
void dijikstra(int G[MAX][MAX], int n, int startnode);
void main(){
int G[MAX][MAX], i, j, n, u;
clrscr();
printf("\nEnter the no. of vertices:: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("\nEnter the adjacency matrix::\n");
for(i=0;i < n;i++)
for(j=0;j < n;j++)
scanf("%d", &G[i][j]);
printf("\nEnter the starting node:: ");
scanf("%d", &u);
dijikstra(G,n,u);
getch();
}
void dijikstra(int G[MAX][MAX], int n, int startnode)
{
int cost[MAX][MAX], distance[MAX], pred[MAX];
int visited[MAX], count, mindistance, nextnode, i,j;
for(i=0;i < n;i++)
for(j=0;j < n;j++)
if(G[i][j]==0)
cost[i][j]=INFINITY;
else
cost[i][j]=G[i][j];
for(i=0;i< n;i++)
{
distance[i]=cost[startnode][i];
pred[i]=startnode;
visited[i]=0;
}
distance[startnode]=0;
visited[startnode]=1;
count=1;
while(count < n-1){
mindistance=INFINITY;
for(i=0;i < n;i++)
if(distance[i] < mindistance&&!visited[i])
{
mindistance=distance[i];
nextnode=i;
}
visited[nextnode]=1;
for(i=0;i < n;i++)
if(!visited[i])
if(mindistance+cost[nextnode][i] < distance[i])
{
distance[i]=mindistance+cost[nextnode][i];
pred[i]=nextnode;
}
count++;
}
for(i=0;i < n;i++)
if(i!=startnode)
{
printf("\nDistance of %d = %d", i, distance[i]);
printf("\nPath = %d", i);
j=i;
do
{
j=pred[j];
printf(" <-%d", j);
}
while(j!=startnode);
}
}
output