Introduction of 8237
- Direct Memory Access (DMA) is a method of allowing data to be moved from one location to another in a computer without intervention from the central processor (CPU).
- It is also a fast way of transferring data within (and sometimes between) computer.
- The DMA I/O technique provides direct access to the memory while the microprocessor is temporarily disabled.
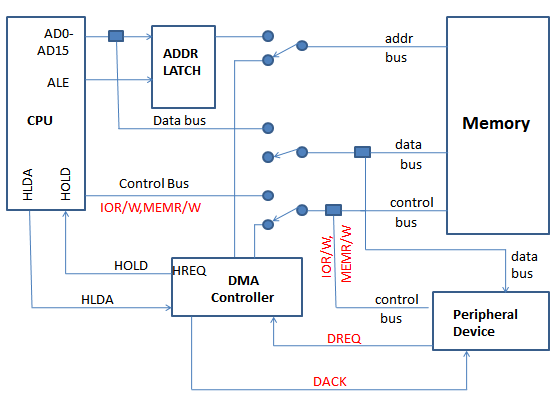
- The DMA controller temporarily borrows the address bus, data bus and control bus from the microprocessor and transfers the data directly from the external devices to a series of memory locations (and vice versa).
- Two control signals are used to request and acknowledge a direct memory access (DMA) transfer in the microprocessor-based system.
- The HOLD signal as an input(to the processor) is used to request a DMA action.
- The HLDA signal as an output that acknowledges the DMA action.
- When the processor recognizes the hold, it stops its execution and enters hold cycles.
- HOLD input has higher priority than INTR or NMI.
- The only microprocessor pin that has a higher priority than a HOLD is the RESET pin.
- HLDA becomes active to indicate that the processor has placed its buses at high-impedance state.
- Direct memory accesses normally occur between an I/O device and memory without the use of the microprocessor.
- A DMA read transfers data from the memory to the I/O device.
- A DMA write transfers data from an I/O device to memory.
- The system contains separate memory and I/O control signals.
- Hence the Memory & the I/O are controlled simultaneously
- The DMA controller provides memory with its address, and the controller signal selects the I/O device during the transfer.
- Data transfer speed is determined by speed of the memory device or a DMA controller.
- In many cases, the DMA controller slows the speed of the system when transfers occur.
- The serial PCI (Peripheral Component Interface) Express bus transfers data at rates exceeding DMA transfers.
- This in modern systems has made DMA is less important.
Basic DMA Operation:
Basic DMA Definitions
CPU having the control over the bus

When DMA operates
The 8237 DMA Controller
- The 8237 supplies memory & I/O with control signals and memory address information during the DMA transfer.
- It is actually a special-purpose microprocessor whose job is high-speed data transfer between memory and I/O
