What is Cryptography?
Cryptography is the art and science of making a cryptosystem that is capable of providing information security.
Cryptography deals with the actual securing of digital data. It refers to the design of mechanisms based on mathematical algorithms that provide fundamental information security services. You can think of cryptography as the establishment of a large toolkit containing different techniques in security applications.
What is Cryptanalysis?
The art and science of breaking the cipher text is known as cryptanalysis.
Cryptanalysis is the sister branch of cryptography and they both co-exist. The cryptographic process results in the cipher text for transmission or storage. It involves the study of cryptographic mechanism with the intention to break them. Cryptanalysis is also used during the design of the new cryptographic techniques to test their security strengths.
Note − Cryptography concerns with the design of cryptosystems, while cryptanalysis studies the breaking of cryptosystems.
Security Services of Cryptography
The primary objective of using cryptography is to provide the following four fundamental information security services. Let us now see the possible goals intended to be fulfilled by cryptography.
Confidentiality
Confidentiality is the fundamental security service provided by cryptography. It is a security service that keeps the information from an unauthorized person. It is sometimes referred to as privacy or secrecy.
Confidentiality can be achieved through numerous means starting from physical securing to the use of mathematical algorithms for data encryption.
Data Integrity
It is security service that deals with identifying any alteration to the data. The data may get modified by an unauthorized entity intentionally or accidently. Integrity service confirms that whether data is intact or not since it was last created, transmitted, or stored by an authorized user.
Data integrity cannot prevent the alteration of data, but provides a means for detecting whether data has been manipulated in an unauthorized manner.
Authentication
Authentication provides the identification of the originator. It confirms to the receiver that the data received has been sent only by an identified and verified sender.
Authentication service has two variants −
Message authentication identifies the originator of the message without any regard router or system that has sent the message.
Entity authentication is assurance that data has been received from a specific entity, say a particular website.
Apart from the originator, authentication may also provide assurance about other parameters related to data such as the date and time of creation/transmission.
Non-repudiation
It is a security service that ensures that an entity cannot refuse the ownership of a previous commitment or an action. It is an assurance that the original creator of the data cannot deny the creation or transmission of the said data to a recipient or third party.
Non-repudiation is a property that is most desirable in situations where there are chances of a dispute over the exchange of data. For example, once an order is placed electronically, a purchaser cannot deny the purchase order, if non-repudiation service was enabled in this transaction.
Cryptography Primitives
Cryptography primitives are nothing but the tools and techniques in Cryptography that can be selectively used to provide a set of desired security services −
- Encryption
- Hash functions
- Message Authentication codes (MAC)
- Digital Signatures
The following table shows the primitives that can achieve a particular security service on their own.
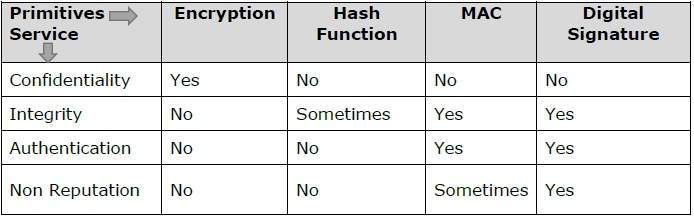
Note − Cryptographic primitives are intricately related and they are often combined to achieve a set of desired security services from a cryptosystem.
